The aim of the competition was to design 5 kindergartens with energy efficient design measures in 5 different locations in Belgrade. Team’s design decision was a unique concept of design as a mutual element for all 5 projects, which is then adjusted to the location’s conditions. Project was awarded with a honourable mention.
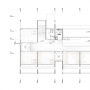
Kindergarten building is designed as a compact volume, defined by the set of perpendicular planes which represent a measurement unit of both the constructive layout and the size of rooms for children. These planes are transformed from full length constructive walls, to framing elements that connect terraces of children’s units and provide shading, and further to elements of paving and playground facilities. In this way a dynamic but controlled relation to the surroundings is achieved. These planes also represent the main design element which defines volumes and functional units, which is a contemporary interpretation of the modernist model of design. In the interior space this separation of volumes is creating different ambients for children, their physical and educational needs. Central interior space consists of double height entrance hall and a multifunctional auditorium which can be joined. All units for children’s reside are connected with this space, either through the corridor in the ground floor or by the over viewing gallery hall.
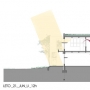
Volume simplicity is also reflected on the functional organization, which is respecting bioclimatic thermal zoning and orientation principles. Units for children’s reside have the best possible orientation depending on the location, while all technical rooms have north orientation. Multifunctional hall and auditorium also have north orientation, in order to prevent overheating problem and provide uniformity of lighting. All rooms in the ground floor and the multifunctional auditorium have the possibility to connect with the adjoining outdoor spaces. Rooms located on the first floor are nursery rooms and classrooms, which have the possibility of connection with the green roof on top of the technical rooms in the ground floor. Natural ventilation is provided throughout the object.
Energy efficiency measures are integrated in the design concept (thermal zoning and volume definition) and also in the detail façade and constructive details study. All elements which are not part of the thermal layer are fully detached from the main volume, both thermally and constructively. All spaces inside the building have natural ventilation and lighting provided. Façade and its elements (light shelves, vertical shading, terraces and overhangs, material color and texture) are designed in a way that diffuse daylighting illumination is improved, while glare effects are fully controlled. Glazing elements are designed with minimum frame percentage in order to further improve daylighting illumination, and also to improve thermal characteristics. Green roofs are implemented because of their insulating properties and also in order to reduce heat island effects. Wood cladding with a ventilated layer as a façade material is used in a combination with façade insulation systems in order to improve thermal characteristics and also as a symbolic representation of ecological architecture with the idea of its presentation in education purposes. Additional alternative energy harvesting systems are considered, depending of the further real development possibilities, such as photovoltaic panels and solar collectors, wind harvesting elements and geothermal energy usage.